Archives of Community Medicine and Public Health
Escalating Dengue in Bangladesh: An Analytical Assessment of Environmental and Socioeconomic Drivers
Alumnus, Faculty of Pharmacy, Dhaka University, Dhaka, Bangladesh
Author and article information
Cite this as
Mohiuddin AK. Escalating Dengue in Bangladesh: An Analytical Assessment of Environmental and Socioeconomic Drivers. Arch Community Med Public Health. 2026;12(1):001-018. Available from: 10.17352/2455-5479.000229
Copyright License
© 2026 Mohiuddin AK. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.Abstract
Dengue has emerged as one of the most severe and rapidly escalating public health threats in Bangladesh, reflecting both localized vulnerabilities and broader global transmission dynamics. This study aims to examine the key environmental, climatic, and socioeconomic drivers underlying the country’s unprecedented dengue surge since 2018, with particular emphasis on post-COVID trends. The central research questions are: (i) how climate variability and urban environmental changes are reshaping dengue transmission in Bangladesh, (ii) which often-overlooked structural factors are intensifying the severity of outbreaks, (iii) how these local dynamics reflect emerging global risks, and (iv) how global risk management practices can be effectively implemented in the Bangladeshi context. Using a comprehensive narrative review of national surveillance data obtained from official sources, peer-reviewed literature, meteorological records, and validated public reports, the study synthesizes evidence on temperature rise, altered rainfall patterns, humidity, unplanned urban growth, population density, sanitation failures, construction activity, pollution, insecticide resistance, and declining green cover. Findings indicate that dengue transmission in Bangladesh is driven by a convergence of climate stressors and human-made environmental conditions, particularly clogged drainage systems, unmanaged plastic waste, water storage practices, and high-rise construction sites that facilitate Aedes mosquito breeding. The study concludes that Bangladesh’s dengue crisis represents an early warning of a wider global emergency. Addressing it requires integrated climate-responsive surveillance, urban planning reforms, strengthened vector control, and coordinated public health action grounded in a One Health approach.
Abbreviations
BI: Breteau Index; DGHS: Directorate General of Health Services; DNCC: Dhaka North City Corporation; DSCC: Dhaka South City Corporation; IEDCR: The Institute of Epidemiology, Disease Control and Research; IVM: Integrated Vector Management; NS1: Nonstructural Protein 1; RAJUK: Rajdhani Unnayan Kartripakkha; WHO: World Health Organization
Introduction
Each year, mosquitoes wage a silent yet devastating war—infecting nearly 700 million people and claiming more than a million lives across the globe [1]. Mosquito-borne viruses like dengue, chikungunya, and Zika have devastated 166 countries over the last five decades, costing nearly $100 billion and surging fourteen-fold between 2013 and 2022 [2]. While malaria continues to devastate Africa—accounting for over 90% of cases reported in the WHO African Region [3]—Asia is grappling with dengue, which is responsible for nearly 70% of global infections [4], with Southeast Asia bearing the heaviest burden [5]. Although the COVID-19 pandemic momentarily disrupted this trajectory, the post-pandemic resurgence of dengue infections reveals its persistent grip on the region [6]. In Bangladesh, dengue remained relatively rare before 2018 but surged thereafter, following global trends, briefly paused during the COVID-19 pandemic, and emerged as the deadliest infectious disease in the post-COVID era, peaking in 2023 (Figure 1). This alarming rise, driven by a combination of meteorological changes and overlooked socioeconomic factors, forms the central focus of this paper.
Data sources and methodology
Data sources and study design
This study employed a narrative-analytical review design integrating epidemiological, climatic, environmental, and socioeconomic evidence to examine dengue transmission dynamics in Bangladesh. Data were drawn from authoritative national sources, including the Directorate General of Health Services (DGHS), the Institute of Epidemiology, Disease Control and Research (IEDCR), and the Bangladesh Meteorological Department, alongside global datasets from WHO and CDC. Peer-reviewed literature indexed in recently published peer-reviewed studies indexed in established databases, including PubMed, Embase, Scopus, Web of Science, and the Cochrane Central Register, as well as leading journals published by Elsevier, Springer, Wiley Online Library, and Wolters Kluwer. Where recent academic data were unavailable, rigorously verified reports from reputable international and national media were used to contextualize rapidly evolving outbreaks.
Quantitative analytical framework
Temporal trends in dengue cases, hospitalizations, and mortality (2000–December 8, 2025) were descriptively analyzed alongside meteorological variables—temperature, rainfall, humidity, and wind speed—since dengue cases and deaths declined significantly from November onward. Patterns were interpreted in relation to established quantitative findings from machine-learning models, time-series analyses, and climate–disease association studies conducted in Bangladesh and comparable tropical settings.
Qualitative synthesis and validation
A thematic synthesis was conducted to integrate qualitative evidence on urbanization, sanitation, waste management, pollution, construction practices, insecticide resistance, and public perception. Cross-validation was achieved by triangulating national surveillance data with international studies and multi-country comparisons, ensuring internal consistency with the literature review and coherence with the study’s discussion and findings.
Literature review
The current global landscape of dengue
Global dengue incidence is rising at an alarming rate. While reported patterns vary, the surge is undeniable. According to WHO, 6.5 million cases and 8,791 deaths were reported globally in 2023 [7], rising to 7.6 million cases and 3,000 deaths by April 2024 [8]. Notably, the US CDC and WHO’s global dengue surveillance system, launched in May 2024, reported 12–13 million cases and over 7,000 deaths in the Americas alone in 2024 [9,10]. Ranked among the WHO’s top ten global health threats, dengue affected approximately 90 countries in 2024, with Brazil bearing the highest burden, followed by Argentina and Mexico [11]. Current WHO estimates suggest that dengue causes up to 400 million infections annually [12], with incidence having increased thirtyfold over the past fifty years [13], now placing 3.9–5.6 billion people—more than half of the world’s population—at risk [14,15]. Moreover, the US CDC reports that half of the global population lives in dengue-risk areas, putting both residents and travelers at risk [16]. Dengue, primarily transmitted by Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus, disproportionately affects the southern hemisphere, making effective tetravalent vaccines critical for global health [17]. Current vaccine development faces challenges in ensuring protection against all serotypes, addressing varied immune responses, and adapting to emerging strains.
Meteorological and socioeconomic factors of dengue transmission
Environmental and socioeconomic factors jointly drive global dengue transmission, with climate conditions like temperature, rainfall, and humidity shaping mosquito habitats, while urbanization, population density, poverty, and inadequate sanitation increase human exposure and vulnerability, as discussed in Table 1.
Key risk factors for dengue in Bangladesh: Insights from previous research
Bangladesh, a tropical country in South Asia situated between 20°–27°N and 88°–93°E, occupies the world’s largest and most densely populated delta—the low-lying Ganges–Brahmaputra Delta, formed by rivers originating in the Himalayas. With more than 1,000 rivers spanning roughly 24,140 km and a coastline along the Bay of Bengal, the nation experiences high humidity and heavy rainfall, making it particularly vulnerable to floods and tropical cyclones [27-29]. Over the past four decades, temperatures in Bangladesh have risen by approximately 0.5 °C, which has lengthened the dengue season and accelerated transmission, with case numbers doubling roughly every decade since 1990. The World Bank notes that dengue infections increase significantly at temperatures between 25 °C and 35 °C, peaking around 32 °C, while global mosquito transmission capacity has grown by up to 9.5% since 1950 [30].
A study published in Oxford Academic on dengue transmission in Bangladesh (2000–2022) found that rising temperatures and shifts in rainfall patterns between 2011 and 2022 were closely linked to increased cases and deaths [31]. Recent climatic shifts have further intensified the risk. From 2022 to 2025, October rainfall in Bangladesh has been highly variable, with a trend toward heavier late-monsoon precipitation. Such changes have prompted entomologists to warn of prolonged dengue outbreaks [32-34]. A comprehensive review of three major medical databases—PubMed, Embase, and Web of Science—up to December 5, 2024, indicates that climate change is reshaping temperature, rainfall, and humidity patterns, thereby expanding the geographic range of dengue and altering exposure risks across different populations [35]. Figure 2 shows that, following the global pattern, dengue cases rise in tandem with increases in temperature, rainfall, and humidity.
Evaluating the various dengue determinants in Bangladesh from 2000 to 2023, researchers from Begum Rokeya University used XGBoost and LightGBM with explainable AI to identify population density, precipitation, temperature, and land-use as key predictors, aligning with recent studies and supporting early-warning systems [36]. A comparative analysis with Singapore found that rainfall fueled dengue transmission in Bangladesh, while humidity and sunshine suppressed it, whereas in Singapore, warmer temperatures drove infections, and rainfall and humidity helped curb spread [37]. Hossain, et al. [38] identified rapid urbanization, climatic suitability, and the persistent presence of Aedes mosquitoes as key drivers of increased human–vector contact and the expanding geographic reach of dengue. Periodic serotype shifts, weak surveillance, limited healthcare capacity, and low public awareness further intensify these risks. Building on this, Khan, et al. [39] highlighted possible post-COVID immune effects, climate variability, dominant viral serotypes, and systemic failures in patient management as contributors to Bangladesh’s recent high fatality rates, underscoring the need for stronger clinical care, more trained personnel, improved vector control, and investment in One Health–based prevention.
Examining seasonal dengue patterns from January 2008 to November 2024, Alam, et al. [40] showed that incidence is tightly linked to meteorological conditions, with peaks strongly correlated with higher temperatures, humidity, rainfall, and wind speed. Their study emphasized the need for future models to integrate real-time meteorological inputs along with urbanization and socioeconomic factors. Islam, et al. [41] similarly argued that combining climate projections with human mobility and socio-environmental variables is essential for forecasting outbreaks and guiding effective prevention strategies. Supporting this, Islam and Hu [42] identified rapid human movement as a major transmission driver in Bangladesh, with festival gatherings, increased mobility, and post-lockdown shifts all associated with higher case burdens. Ogieuhi, et al. [43] noted that poor sanitation, insecticide resistance, limited vaccine access, low public awareness, and mounting healthcare pressures, combined with climate change and rapid urbanization, collectively heighten dengue risks, especially for vulnerable populations.
Common public perception vs. reality
In Bangladesh, dengue perception shows a mix of high awareness of its severity (it's deadly) but low personal risk (susceptibility), leading to inconsistent prevention, with educated urban dwellers often better informed than rural populations. Table 2 offers an overview of dengue-related knowledge, perception, and attitudes across different Bangladeshi populations.
The recent dengue outbreaks, driven by shifting climate patterns, rapid urbanization, dense populations, insecticide resistance, and low public awareness, have severely strained Bangladesh’s healthcare system and economy. While climate change strongly shapes dengue (Flavivirus) transmission, insecticide misuse and rising resistance also play critical roles. WHO has warned that fogging is ineffective against Aedes mosquitoes, underscoring city corporations’ misplaced reliance on mass spraying instead of source reduction, targeted larviciding, and proper vector control? Compounding the problem, widespread metabolic resistance and common kdr mutations have greatly reduced the effectiveness of pyrethroid insecticides, producing very low mosquito mortality even at elevated doses [54-56].
Rainfall influences mosquito growth in complex ways. While light rain creates standing water ideal for breeding, heavy rainfall can destroy breeding sites or wash away larvae, limiting mosquito development. Additionally, wind speed was found to be weakly positively correlated with dengue incidence in Bangladesh. Although many attributed the 2025 outbreak to heavy rainfall, the persistence of dengue had already been evident, with over 320,000 infections and 1,700 deaths recorded in 2023—figures considerably higher than those observed in 2025 (Figure 3). Interestingly, a study conducted in Dhaka revealed that dengue cases actually declined with increasing levels of both rainfall and sunshine, contradicting common public perception [57]. Experts warn that prolonged monsoons and poor waste management have created stagnant water and ecological imbalance, enabling mosquitoes to breed more extensively and intensifying the outbreaks [58].
Discussions and findings
Escalating dengue burden in Bangladesh
Bangladesh is at the epicenter of the crisis, grappling with unprecedented challenges. By 21 September 2025, deaths had surged 150%, and cases had doubled from the previous year [59]. Just two months later, by 23 November, infections had topped 90,000 with fatalities reaching 364 [60]—70% higher than six weeks earlier [61]. Hospital admissions, according to dynamic data from the Directorate General of Health Services (DGHS) [62], nearly quadrupled from 5,951 in June to 22,520 in October 2025, pushing an already fragile healthcare system to the brink (Figure 3).
November 2025 brought the crisis to a new peak: on 18 November alone, over 900 viral fever patients flooded hospitals, joining nearly 3,000 dengue cases already under treatment [63]. Since 2023, more than half a million Bangladeshis have been infected, and over 2,670 have died—marking the deadliest dengue toll in the nation’s history. By the end of November, total cases had surpassed 94,300, hospitalizations had exceeded 92,000, and deaths had risen to 382. November alone recorded more than 24,500 cases and 104 fatalities, meaning that over one-quarter of the year’s infections and deaths occurred in a single, devastating month [62].
Historical data magnify the crisis. Between 2000 and 2022, Bangladesh recorded 853 dengue-related deaths [39,64], yet 2023 alone more than doubled that total, with 1,705 fatalities and over 321,000 infections—the largest annual outbreak on record (Figure 1). The demographic landscape is shifting. In 2023, women represented roughly 40% of dengue cases but accounted for 57% of deaths [65]. By December 8, 2025, men experienced nearly twice as many cases and over half of all deaths (Figure 4). Notably, in 2023, older adults faced disproportionately severe dengue and higher mortality due to immune vulnerability and comorbidities, with each additional decade raising fatality by 30%, whereas by 2025, young adults aged 21–30 accounted for over a quarter of both cases and deaths [62,65]. However, older adolescents and young adults also represented more than half of all cases during the 2016, 2018, and 2019 outbreaks [65].
The overlooked drivers of Bangladesh’s escalating dengue crisis
The recent dengue outbreaks, fueled by changing climate patterns, rapid urbanization, high population density, insecticide resistance, and low public awareness, have placed a severe strain on Bangladesh’s healthcare system and economy. While climate change and urban growth are widely acknowledged as major drivers of the rising dengue burden, several less-discussed factors—often tied to uncontrolled urbanization—have intensified the crisis; these interconnected issues, highlighted in recent international research and media, remain largely overlooked by the public due to limited awareness.
Vegetation loss and rising temperature
Warmer temperatures accelerate mosquito aging, shortening their lifespan and altering infection patterns [66]. Yet, over successive generations, heat-exposed mosquitoes can develop greater tolerance to viruses without losing vitality, a recent study shows [67]. Global warming has thus become a “perfect storm” for mosquito-borne diseases, affecting every stage of transmission [68].
Urbanization-driven loss of natural vegetation further elevates dengue risk, as areas with reduced green cover provide ideal conditions for mosquito breeding and disease spread, as demonstrated in studies from Mexico [69] and Brazil [70]. In Amazonian Brazil, for example, deforestation of just one square kilometer was linked to 27 additional malaria cases [71].
Between 1989 and 2020, Dhaka lost more than half of its green cover due to rapid urban growth, triggering a significant rise in temperatures [72]. Over three decades, the number of extreme heat days (≥35 °C) nearly doubled, making Dhaka one of the fastest-warming cities in the world, according to the International Institute for Environment and Development [73]. Furthermore, the World Bank reports that the city’s heat index has increased more than 65% faster than the national average [74]. These hotter, denser conditions let Aedes mosquitoes adapt to heat, building stronger virus tolerance and becoming even more efficient carriers [63]. A climate projection from a decade ago indicates that, without adaptation, a 3.3 °C increase by 2100 could result in more than 16,000 additional dengue cases [75].
Population density, poor sanitation, and waste disposal
Rapid urbanization and extreme population density in Bangladesh are creating ideal conditions for intensified dengue transmission. In overcrowded cities with inadequate sanitation, stagnant water accumulates easily, offering abundant breeding sites for Aedes mosquitoes. Dhaka—home to more than 75,000 people per square mile [76]—is now the world’s second most densely populated city [77], and its tightly packed, human-built landscape accelerates Aedes aegypti growth, reproduction, and survival far more than suburban or rural settings [78]. Monsoon-season spikes in heat, humidity, and rainfall further amplify this risk, with 2019 data showing that nearly 90% of dengue cases erupted between June and October, overwhelmingly concentrated in the city’s hottest, most densely built neighborhoods [79]. Dengue hotspots consistently emerge where population density is highest, particularly in Thanas such as Badda, Jatrabari, Kadamtali, Mirpur, Mohammadpur, Sobujbagh, Shyampur, Tejgaon, Dhanmondi, and Uttara, where close human–mosquito contact further amplifies transmission [80].
In Bangladesh, roughly 40% of the population lives in urban areas, with over half residing in densely packed slums [81]. Communities without adequate sanitation—especially in these overcrowded settlements—are highly vulnerable to mosquito-borne diseases such as dengue and chikungunya [82]. Dhaka’s congested neighborhoods, compounded by poor sanitation, provide abundant stagnant water, creating ideal breeding grounds for mosquitoes. More than one-third of the population still lacks access to safely managed sanitation, and UNICEF estimates that about 230 tons of fecal waste enter Dhaka’s 4,500-kilometer drainage network every day. The system is already 70% clogged with trash and debris because of poor infrastructure and longstanding neglect, according to the Institute of Water Modelling [83,84]. As a result, even moderate rainfall creates stagnant, mosquito-infested pools—a problem further intensified by flooding and extreme weather across both urban and rural areas [85]. Additionally, in many dense urban neighborhoods, inconsistent water supply forces residents to store water in containers [43], a practice well documented in neighboring India, further increasing the risk of mosquito-borne diseases [86].
Poor waste management is a critical driver of dengue risk among both children and adults—and in urban Bangladesh, this threat looms large. Shockingly, 55% of solid waste in urban areas remains uncollected, creating ideal breeding grounds for the mosquitoes that spread the disease [87]. Evidence from urban Thiruvanathapuram, South India, indicates that inadequate waste management infrastructure can be associated with a 40% higher incidence of dengue and chikungunya cases [88]. Likewise, studies in informal urban settlements in Indonesia and Fiji reported that by age 4–5, over half of children had already been infected, highlighting how insufficient waste disposal accelerates early exposure to dengue [89].
Pollution as a trigger for viral resistance and mosquito dynamics
The WHO estimates that nearly a quarter of human diseases and deaths stem from long-term exposure to pollution [90]. While research on environmental impacts on dengue in Bangladesh remains limited, international studies underscore their significance. Recent findings from cities in Taiwan [91], Singapore [92], Guangzhou [93], Upper Northern Thailand [94], Melaka, Malaysia [95], and Greater São Paulo [96] demonstrate that air pollutants—such as particulate matter PM2.5, SO₂, O₃, CO, and NOx—interact with climate factors to influence mosquito populations, viral activity, and human immunity to the virus. These impacts, however, vary depending on pollutant type, concentration, and region, often producing complex, non-linear effects on mosquito dynamics. Interestingly, a study covering 76 provinces in Thailand from 2003 to 2021 found that higher surface concentrations of SO₂ and PM2.5 were generally associated with lower incidences of dengue, malaria, chikungunya, and Japanese encephalitis, likely due to adverse effects on mosquito survival and behavior [97]. These findings highlight the need for further research.
A Lancet study reported that improperly discarded plastics accumulate stagnant water, creating ideal breeding sites for Aedes mosquitoes that transmit dengue, Zika, chikungunya, and yellow fever, thereby directly increasing vector populations. Indirectly, plastic debris also clogs drainage systems, producing large stagnant pools that promote mosquito proliferation and elevate the risk of diseases such as malaria [98]. Bangladesh is now experiencing an alarming rise in microplastic pollution. Just three rivers--Meghna, Karnaphuli, and Rupsha discharge nearly one million metric tons of mismanaged plastic each year [99]. In total, 36 rivers in Bangladesh are among the 1,656 waterways worldwide responsible for 80% of global riverine plastic emissions [100]. Per-capita plastic consumption has tripled—from 9 kg in 2005 to 2020—while COVID-19 contributed an additional 78,000 tons in a single year, according to a 2021 report by the Environment and Social Development Organization (ESDO) [101].
In Dhaka, per-capita use reaches 24 kg, and nearly one-eighth of all plastic waste ends up in canals and rivers. An estimated 23,000 to 36,000 tons of plastic waste accumulate annually across 1,212 dumping hotspots surrounding the Buriganga, Turag, Balu, and Shitalakhsya rivers, a trend highlighted by a former World Bank country director during a program in Dhaka [102]. Beyond environmental degradation, this rising plastic burden may intensify mosquito-borne disease risks: researchers from the Beijing Institute of Microbiology and Epidemiology show that mosquitoes exposed to microplastics can transfer them to mammals, develop altered gut microbiomes, experience delayed development, and exhibit reduced insecticide susceptibility—factors that could heighten disease transmission [103]. Also, microplastics can adsorb pyrethroid insecticides such as deltamethrin, reducing the concentration available to act on mosquitoes. However, because the findings rely on a single study and other research shows conflicting results, more evidence is needed to clarify how microplastic exposure influences mosquito dynamics and dengue transmission.
Construction sites and high-rises: Major breeding grounds driving dengue in Dhaka
Dhaka’s rapid and largely unplanned urban expansion has transformed the city into a highly conducive environment for Aedes mosquito proliferation. Numerous under-construction buildings, left exposed to the elements, now serve as prime breeding grounds for the vectors of dengue. Surveys indicate that, in the decade preceding 2016, an average of 95,000 new structures were erected annually within the jurisdiction of the Rajdhani Unnayan Kartripakkha (RAJUK). Over the subsequent fifteen years, at least 64,000 additional buildings were constructed across the capital [104,105]. In July 2020, inspections conducted by the Dhaka North City Corporation (DNCC) revealed that nearly 70% (8,764 out of 12,619) of homes and construction sites surveyed across 55 wards harbored potential Aedes breeding sources [106]. These inspections were carried out in collaboration with the National Malaria Elimination and Aedes Transmitted Disease Control Programme under the Directorate General of Health Services (DGHS).
The following year, the situation deteriorated further. A 2021 DGHS study covering 70 areas of Dhaka reported alarming Aedes densities, with the Breteau Index (BI)—the number of water-holding containers infested with larvae per 100 houses—rising to 23.3 in Lalmatia and Iqbal Road (Ward 32, DNCC) and 20.0 in Sayedabad and Uttar Jatrabari (Ward 48, DSCC). High-rise buildings accounted for over 45% of breeding sites, followed by under-construction structures at nearly 35% [107]. In 2024, the former Mayor of DSCC warned that construction would be halted wherever Aedes larvae were detected and that dengue control drives would be launched in advance of the rainy season, alongside the government’s seven-year National Dengue Prevention and Control Strategy [108]. The most recent pre-monsoon survey, conducted jointly by the DGHS Communicable Disease Control Programme and the Institute of Epidemiology, Disease Control and Research (IEDCR), presents a similarly concerning picture: multistory buildings accounted for almost 60% of Aedes larvae, with a further 20% found in under-construction sites [109].
From neglect to epidemic: How policy failures worsened dengue in Bangladesh
Bangladesh’s authorities have repeatedly failed to curb Aedes populations, persisting with outdated chemical approaches while neglecting structural determinants and community-level interventions. Government action has remained fragmented and reactive; in 2023, officials proved unable to control Aedes mosquitoes, opting instead to fault households and impose ethically questionable fines. Such mismanagement and flawed strategies have allowed dengue transmission to escalate unchecked, rendering official prevention efforts largely performative (Figure 5). Transparency International Bangladesh has identified several drivers of high mortality, including inadequate hospital staffing, delayed diagnoses, false-negative NS1 results, weak vector-control measures, and limited healthcare capacity beyond Dhaka [110]. Experts further warn that the absence of strategic planning, non-adherence to WHO guidelines, and the failure to involve qualified public-health professionals have deepened the crisis. By 2024, South Asia was experiencing its most severe dengue epidemic on record, with Bangladesh and India reporting thousands of deaths as hospitals were overwhelmed. Concerns have mounted over inadequate anti-mosquito measures and the near absence of public awareness campaigns, shortcomings partly attributed to the lack of elected union parishad leadership under the interim government. Yet Dhaka’s two city corporations have spent more than BDT 1,000 crore (over USD 81 million) on mosquito-control programs in the past decade, even as the capital continues to account for the majority of infections and fatalities [111]. In 2023 alone, Dhaka recorded more than half of all cases and nearly 70 per cent of fatalities, underscoring that vector-borne outbreaks transcend partisan boundaries [112]. In FY 2024–25, Dhaka South City Corporation spent less than 40 per cent of its overall budget despite increasing its mosquito-control allocation by 19% [113]. Weak implementation, poor coordination, obsolete operational strategies, and persistent shortages of chemicals and manpower have severely undermined larviciding, mosquito-control, and drain-cleaning activities.
Results and recommendation
Aligned with WHO policy and reflecting the 'think global, act local' approach, addressing Bangladesh’s dengue surge requires moving away from reactive, chemical-heavy measures toward a One Health–based Integrated Vector Management (IVM) strategy, which incorporates public health safeguards into urban planning, water storage, sanitation, waste management, drainage, and environmental governance. Strengthening surveillance-led action, evidence-based budgeting, trained frontline health workers, sustained risk communication, and community participation is essential to move from crisis response to prevention, particularly in densely populated and climate-vulnerable urban settings. Given shared climatic risks and population mobility, scientific innovation and cross-border collaboration are critical to ensuring sustainable, regionally coordinated dengue control in Bangladesh.
Urban planning reforms
Bangladesh’s dengue surge has been closely linked to unplanned urban expansion, particularly in Dhaka, where high-rise buildings, dense settlements, and construction sites dominate the landscape. Urban planning reforms must prioritize climate-responsive zoning, mandatory drainage design, and mosquito-safe construction codes, especially for multistory and under-construction buildings that currently account for most Aedes breeding sites. In addition, biodiversity favors the regulation of the movement of disease vectors and thus promotes resilience to epidemics [114,115]. Cities like Singapore and parts of Rio de Janeiro have reduced dengue risk by integrating vector control considerations into building permits, land-use planning, and housing design [116-118]—an approach Bangladesh urgently needs to adopt. Without embedding public-health safeguards into urban development, rapid urbanization will continue to amplify dengue transmission rather than support sustainable growth.
Caution on water storage
Irregular municipal water supply in many Bangladeshi cities forces most of the households to store water in drums, buckets, and tanks, which are major breeding sites for Aedes mosquitoes. Public health guidance must emphasize covering, cleaning, and frequently emptying water containers, particularly during the monsoon and post-monsoon seasons when dengue peaks. Similar initiatives in Chennai [119], Bengaluru [120], Makassar [121], Maros Regency [122], and Yogyakarta [123] have focused on community-based monitoring of household water storage and the promotion of affordable container covers to prevent mosquito breeding. In Bangladesh, caution on water storage must be framed as a necessity driven by infrastructure gaps, not merely as individual negligence.
Ensuring optimum sanitation facilities
PooSanitation continues to drive dengue risk in Bangladesh, particularly in densely populated urban slums where safely managed sanitation remains inaccessible for many residents. Overflowing latrines, open drains, and leaking wastewater create stagnant water pools, indirectly promoting mosquito breeding. Evidence from Vietnam indicates that expanding sanitation coverage can substantially reduce mosquito breeding habitats even without extensive chemical control [124]. Furthermore, training sanitation workers has been shown to enhance knowledge and practices for dengue prevention, reflecting similar experiences in India, though challenges remain in community engagement and ensuring worker safety [125]. Strengthening sanitation infrastructure in Bangladesh is therefore not only a matter of public health and development but also a vital strategy for dengue prevention.
Proper disposal of solid waste
More than half of urban solid waste in Bangladesh remains uncollected, allowing plastic containers, packaging, and discarded items to trap rainwater and create ideal mosquito breeding sites. Improper waste disposal has been repeatedly identified as a major contributor to dengue outbreaks in Bangladesh, particularly in Dhaka’s canals and drainage systems. Evidence from Gampaha district of Sri Lanka [126], urban areas of Malaysia [127], and informal urban settlements in Indonesia and Fiji [89] indicates that improved waste segregation and regular collection can lower dengue incidence by reducing mosquito breeding habitats. In Bangladesh, effective solid-waste management must be treated as a public-health intervention rather than a purely municipal service.
Sustainable drainage system
Dhaka’s City Corporations (DNCC and DSCC), together with other responsible authorities, frequently issue tenders for drainage works or interventions on drainage infrastructure—often annually or even multiple times within a single year—raising concerns about repetitive public spending and the potential waste of public funds [127-132]. These recurring projects are widely attributed to poor planning and design, corruption, and inadequate maintenance, which have allowed chronic problems such as waterlogging to persist despite ongoing construction. The repeated disruptions also cause significant inconvenience to daily travel and urban life. Implementing well-planned, modern drainage designs with high-quality standard materials, along with the involvement of trained engineers and skilled labor, can help establish a sustainable sewage system and minimize the need for repeated interventions—measures that have proven effective in controlling vector-borne diseases [133-137], as highlighted in various scholarly articles and WHO guidelines.
Regular drainage and clog prevention
Bangladesh’s drainage networks—especially in Dhaka—are heavily clogged with plastic, debris, and fecal waste, causing stagnant water even after moderate rainfall. This chronic drainage failure has turned canals and roadside drains into persistent mosquito reservoirs, extending dengue transmission beyond the monsoon season. Studies in urban areas of Jakarta, Surabaya, Bandung, and Presidente Prudente in São Paulo have found a strong link between dengue incidence and poorly maintained storm drains [138,139]. In contrast, a simple, community-driven modification of storm drains in Salvador, Brazil, effectively prevented water stagnation and resulted in a substantial reduction in both immature and adult Aedes aegypti populations [140]. In Bangladesh, city corporations need to be further strengthened and held more accountable for routinely monitoring waterlogging caused by waste accumulation in drainage systems. However, local authorities alone cannot ensure effective and sustainable drainage without active public participation. Raising strong public awareness about the health consequences of clogged drains, together with consistent and visible enforcement of penalties, is essential for achieving lasting impact. Although privatization may offer a more efficient management solution, bureaucratic obstacles continue to pose significant challenges. For example, the city of Ludhiana in India recently saw its municipal authorities issue tenders for the operation and maintenance of the sewerage system through a small-scale pilot project [141].
Evidence-based budget utilization and monitoring framework development
Despite substantial spending on mosquito control, Bangladesh has achieved limited results because of weak implementation, poor coordination, and an overreliance on ineffective fogging rather than proven source reduction and surveillance-based strategies [54,111,142,143]. A recent systematic review by Low, et al. [144] found insufficient evidence to recommend any single conventional dengue vector control method, underscoring the need for urgent trials of novel approaches. Evidence from Australia, Brazil, and Indonesia shows that Wolbachia-mediated interventions can deliver sustained dengue reduction with major healthcare and productivity savings, making them especially cost-effective in dense urban centers like Dhaka [145]. In parallel, ovitrap-based surveillance is a rapid, low-cost, and sensitive tool, proven effective in settings such as Semarang, Indonesia, and Guangzhou, China [146,147]. Bangladesh, therefore, urgently needs a transparent, data-driven monitoring framework to ensure dengue control resources are used efficiently and equitably.
Integrated vector management practices
Bangladesh’s heavy reliance on chemicals has been largely ineffective due to widespread insecticide resistance in Aedes mosquitoes [55,56]. Following WHO’s Global Technical Strategy, vector control in countries like Bhutan, Malaysia, the Philippines, and Sri Lanka relied on surveillance and interventions but was limited by weak targeting and lack of evidence-based implementation [148]. Since 2001, the WHO has been promoting, and in 2004, it adopted IVM globally for all vector-borne diseases [149]. Combining environmental management, targeted larviciding, biological control, and community participation, IVM offers a more sustainable approach. WHO-guided IVM has succeeded in urban Malaysia [150], Sri Lanka’s Gampaha district [151], Tharu village, Chitwan, Nepal [152], and Zambia [153], reducing mosquito-borne illnesses through source reduction and surveillance-driven measures rather than broad chemical use. For Bangladesh, adopting IVM is essential to overcome insecticide resistance and adapt to changing climates. Although included in the National Dengue Prevention and Control Strategy (2024–2030) [154], its success will rely on sustained political commitment, sufficient resources, and effective implementation.
Training health facilitators
The dengue crisis has exposed gaps in frontline health capacity, including delayed diagnosis, mismanagement of cases, and inadequate referral systems outside major cities [155-158]. Recent years have seen dengue cases requiring increased hospitalizations, as reported both globally and in Bangladesh. Notably, during the 2023 outbreak, over two-thirds of dengue-related deaths occurred within a day of hospital admission, suggesting either rapid disease progression or delayed medical care [159]. Training health facilitators—community health workers, nurses, and primary-care providers—in early dengue recognition and case management can significantly reduce mortality [160-162]. Southern Thailand has achieved improved outcomes by integrating dengue-specific training into primary healthcare systems, although continued training for village health volunteers remains necessary [163,164]. In Bangladesh, strengthening health facilitator capacity is critical, especially during peak transmission months when hospitals are overwhelmed.
Public awareness campaigns
Although dengue awareness is relatively high in Bangladesh, preventive practices remain inconsistent due to misconceptions and low perceived personal risk [46,48-50,165]. Public campaigns should go beyond seasonal messaging and promote year-round behavior change, especially regarding water storage, waste disposal, and early healthcare seeking [43,166-170]. Successful programs in Indonesia [171], India [172], southern Thailand [173], and Singapore [174] combine mass media, neighborhood engagement, videos, social media, mobile apps, and school-based education. A 2024 review by Dapari et al. also found that school-based education effectively raises knowledge and improves dengue prevention practices [175]. In Bangladesh, sustained, evidence-based communication—through schools, health authorities, NGOs, religious institutions, and community leaders—is essential to turn awareness into effective action against dengue.
Environmental management and community capacity building
Environmental degradation—loss of green cover, pollution, and unmanaged urban growth—has intensified dengue risk in Bangladesh by altering mosquito ecology. Community-led environmental management—such as cleaning neighborhood containers and shared spaces, as well as monitoring mosquito breeding sites—has proven effective in Yogyakarta, Indonesia [123]; Fortaleza in northeast Brazil [176]; among Myanmar migrants in Samut Sakhon Province, Thailand [177]; and Singapore [178]. Building community capacity empowers residents to address local risk factors that municipal systems cannot fully cover. In Bangladesh, engaging communities is especially vital in slums and dense neighborhoods where formal services are limited.
Real-time reporting and surveillance for disease trend
Weak and delayed surveillance has hindered Bangladesh’s ability to anticipate and respond to dengue outbreaks effectively. Integrating real-time disease reporting with meteorological and environmental data can enable early warnings and targeted interventions. Countries like Thailand, Singapore, and France, among many other countries, use climate-linked surveillance systems to predict outbreaks weeks in advance. Both countries use a variety of modeling techniques, including machine learning (like XGBoost and LASSO regression) and statistical models, to analyze the complex relationships between these variables and dengue transmission dynamics [179,180]. For Bangladesh, strengthening real-time surveillance is crucial to shift from reactive crisis management to proactive prevention.
Scientific innovation for mosquito control
Traditional dengue control methods are becoming increasingly inadequate in Bangladesh due to rising insecticide resistance and environmental changes. Scientific innovations offer promising alternatives, including biological control—such as Wolbachia-based interventions, which have proven effective in Australia, Brazil, and Indonesia [145]; improved larvicides—like biological agents Bacillus thuringiensis israelensis and diflubenzuron, which have shown strong efficacy against Aedes larvae and provide sustainable alternatives to conventional chemicals in Lao PDR [181]; and novel mosquito management technologies—such as Sterile Insect Technology, where releasing sterile male mosquitoes in Ortigueira, Paraná, Brazil, significantly reduced Aedes aegypti populations and prevented dengue outbreaks [182]. Technology-enabled mosquito monitoring, integrating IoT and machine learning with traditional ovitraps [183], also shows promise. While resource limitations remain, targeted pilot programs could evaluate feasibility under Bangladeshi conditions. Investing in these innovations is essential to future-proof dengue control strategies against climate-driven transmission.
Cross-border collaboration with neighboring countries
Dengue transmission in Bangladesh does not occur in isolation, as climate patterns, human mobility, and viral circulation extend across borders with India and other South Asian countries. Cross-border data sharing, joint surveillance, and coordinated response strategies have been effective in parts of Southeast Asia [184-187]. Given Bangladesh’s dense population and high mobility during festivals and seasonal migration, regional collaboration is particularly important (Figure 6). Strengthening cross-border cooperation can help Bangladesh anticipate emerging risks and align control strategies with regional realities.
Conclusion
In Bangladesh, rising temperatures, unplanned urban expansion, and worsening pollution have created conditions that strongly favor mosquito proliferation, turning rapid development into a relentless battle against one of the country’s deadliest tiny predators. The persistent and evolving threat of dengue underscores the need for timely hospitalization—because the illness can deteriorate quickly—as well as systematic research to understand how environmental pollution, climate variability, and extensive pesticide use are shaping viral resistance and mosquito behavior. Media coverage has largely failed to capture the severity of the crisis, and domestic research remains limited, often attributing outbreaks only to erratic rainfall, monsoon shifts, and stagnant water.
These grim outcomes point to deeper systemic failures, including a lack of public awareness, inadequate hospital staffing, limited healthcare capacity, delayed diagnoses, weak and poorly coordinated vector-control measures, insecticide resistance, limited access to effective vaccines, the absence of strategic planning, failure to follow WHO guidelines, and persistent corruption and negligence, all compounded by the exclusion of qualified public health professionals from decision-making.
Yet evidence from regions with similar dengue patterns points to several overlooked drivers, including air pollution, pesticide and microplastic resistance, and the complex interactions between rapid urbanization and mosquito ecology. With low levels of health literacy, even strong research rarely translates into public awareness or policy reform, and progress in evidence-based studies remains slow. Coordinated efforts that combine early clinical care with rigorous scientific investigation are therefore essential to mitigating the country’s growing dengue burden.
This national tragedy is part of a much larger global shift. A study in Nature warns that by 2080, nearly three in five people could be at risk of dengue [188]. Last year alone, more than fourteen million people were infected worldwide—twice the previous year and twelve times higher than a decade ago [189,190]. As climate instability, unplanned urbanization, and expanding mosquito habitats intensify, dengue is no longer a regional challenge—it is an emerging pandemic that demands urgent international action. The time to act is now, before a greater catastrophe unfolds and more lives are lost.
Data availability statement
The data used in this study were obtained from the Dengue Dynamic Dashboard for Bangladesh, maintained by the Directorate General of Health Services (DGHS), Health Emergency Operation Center & Control Room. These data are publicly available at: https://dashboard.dghs.gov.bd/pages/heoc_dengue_v1.php
References
- Akour A, Bardaweel S, Awwad O, Al-Muhaissen S, Hussein R. Impact of a pharmacist-provided information booklet on knowledge and attitudes towards oral contraception among Jordanian women: an interventional study. Eur J Contracept Reprod Health Care. 2017;22(6):459-64. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1080/13625187.2017.1412425
- AlHamawi R, Khader Y, Al Nsour M, AlQutob R, Badran E. Family planning interventions in Jordan: A scoping review. Women's Health (Lond). 2023;19. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1177/17455057231170977
- Ali M. Ensuring contraceptive security through effective supply chains. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2017. Available from: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/WHO-RHR-17.09
- Ali M, Bellows B. Ensuring adequate financing of family planning commodities and services: Family Planning Evidence Brief. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2018. Available from: https://knowledgecommons.popcouncil.org/departments_sbsr-rh/219/
- Alkhalili M, Al-Hmaid Y, Kheirallah K, Mehaisen L. Assessment of knowledge of sexual reproductive health among female university students in Jordan. Cureus. 2024;16(2):e53386. Available from: https://doi.org/10.7759/cureus.53386
- Alspaugh A, Spatz D, Sommers MS. Women's contraceptive perceptions, beliefs, and attitudes: An integrative review of qualitative research. J Midwifery Women's Health. 2020;65(1):64-84. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1111/jmwh.12992
- Altare C, Delbiso TD, Rodriguez-Llanes JM, Guha-Sapir D, Musa Khalifa A, Spiegel P. COVID-19 epidemiology and changes in health service utilization in Azraq and Zaatari refugee camps in Jordan: A retrospective cohort study. PLoS Med. 2022;19(5):e1003993. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.1003993
- Alyahya MS, Hijazi HH, Alshraideh HA, Al-Sheyab NA, Alomari D, Malkawi S, et al. Do modern family planning methods impact women's quality of life? Jordanian women's perspective. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2019;17(1):154. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12955-019-1226-6
- Amiri M, Khosravi A, Chaman R, Sadeghi E, Mirzaei H, Khanjani N. An overview of the sexual and reproductive health status and service delivery among Syrian refugees in Jordan, nine years since the crisis. Reprod Health. 2020;17(1):166. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12978-020-01005-7
- Anderson K. Daring to ask, listen and act: A snapshot of the impacts of COVID-19 on women and girls' rights and sexual and reproductive health. Amman: United Nations Population Fund (UNFPA) – Jordan; 2020. Available from: https://jordan.unfpa.org/en/publications/daring-ask-listen-and-act-snapshot-impacts-covid-womens-and-girls-rights-and-sexual
- Aolymat I. A cross-sectional study of the impact of COVID-19 on domestic violence, menstruation, genital tract health, and contraception use among women in Jordan. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2021;104(2):519-25. Available from: https://doi.org/10.4269/ajtmh.20-1269
- Aolymat I, Abdul Kadir L, Al Nsour M, Taha H. The impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on female sexual function in Jordan: Cross-sectional study. JMIR Form Res. 2023;7:e40772. Available from: https://doi.org/10.2196/40772
- Asali F, Khuza'a D, Bataineh H, Alsayaideh B, Abbadi R, Zurgan Z. Impact of the coronavirus 19 pandemic on contraception in Jordan. J Obstet Gynaecol. 2022;42(6):2292-6. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1080/01443615.2022.2040969
- Bellows B, Hamilton M, Lemaire J, Mubita-Ngoma C, Duvall S. Family planning vouchers to improve delivery and uptake of contraception in low- and middle-income countries: A systematic review. Lusaka: Population Council; 2016;47(4):357–370. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1111/sifp.12006
- Berdzuli N, Ketting E, Reiss K, Shaffer N, Broutet N, Obst-Reiter B. Ten best public and private sector practices in reproductive health and family planning in the Europe and Eurasia region. Arlington, VA: USAID | DELIVER PROJECT; 2008.
- Boydell V, Schaaf M, George A, Khosla R. Civil society involvement in family planning: A review of global programming and evidence. New York: Population Council; 2017. Available from: https://knowledgecommons.popcouncil.org/departments_sbsr-rh/1725/
- Brahmi D, Steenland MW, Renner RM, Gaffield ME, Curtis KM. Pregnancy outcomes with an IUD in situ: A systematic review. Contraception. 2012;85(2):131-9. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.contraception.2011.06.010
- Butler N, Mokdad A, Newby K. Key considerations for integrating COVID-19 vaccination services: Insights from Iraq and Syria for the MENA region. Social Science in Humanitarian Action (SSHAP); 2022. Available from: https://www.socialscienceinaction.org/resources/key-considerations-for-integrating-covid-19-vaccination-services-insights-from-iraq-and-syria-for-the-mena-region/
- Cottingham J, Germain A, Hunt P. Use of human rights to meet the unmet need for family planning. Lancet. 2012;380(9837):172-80. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(12)60732-6
- De Regt MC. Syrian refugee youth in Jordan: Early marriages in perspective. The Hague: I-WOTRO SRH Programme; 2021. Available from: https://rdfmsc.yu.edu.jo/index.php/en/policy-papers/3982-syrian-refugee-youth-in-jordan-early-marriages-in-perspective
- Department of Statistics (DoS) [Jordan] and ICF. Jordan population, family, and health survey 2023. Amman, Jordan, and Rockville, MD: DoS and ICF; 2024. Available from: https://dhsprogram.com/pubs/pdf/FR388/FR388.pdf
- Department of Statistics (DoS) [Jordan] and ICF. Jordan population and family health survey 2017–18. Amman, Jordan, and Rockville, MD: DoS and ICF; 2019. Available from: https://dhsprogram.com/pubs/pdf/SR256/SR256.pdf
- DHS Program. Further analysis of family planning in Jordan: An analysis brief from The DHS Program [Internet]. 2019 [cited 2024 Dec 5]. Available from: https://dhsprogram.com/pubs/pdf/OD79/AB19.pdf
- El Bizri L, Naja F, Kassir A, Jarrar LG, Ali WKA, Omar AH. The role of community pharmacists in increasing access and use of self-care interventions for sexual and reproductive health in the Eastern Mediterranean region: Examples from Egypt, Jordan, Lebanon, and Somalia. Health Res Policy Syst. 2021;19(Suppl 1):49. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12961-021-00695-0
- El-Dirani Z, Akik C, Attel L, Kamhawi R, Nawafleh M, Essaid A, DeJong J. Interactive community-based theatre to address social barriers to accessing reproductive health services in patriarchal societies: The case of Jordan. Cult Health Sex. 2023;25(2):176-91. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1080/13691058.2022.2029572
- Fry D, Fang X, Elliott S. A qualitative study on the underlying social norms and economic causes that lead to child marriage in Jordan. Amman: UNICEF; 2019. Available from: https://doi.org/10.13140/RG.2.2.35092.78723
- FP2030, UNFPA, and What Works Association. The comprehensive human rights-based, voluntary family planning program framework. London: FP2030; 2021. Available from: https://www.fp2030.org/resources/the-comprehensive-human-rights-based-voluntary-family-planning-program-framework/
- Gausman J, Othman A, Dababnah A, Dabobe M, Suliman A, Langer A. Landscape analysis of family planning research, programmes and policies targeting young people in Jordan: Stakeholder assessment and systematic review. East Mediterr Health J. 2020;26(9):1115-34. Available from: https://doi.org/10.26719/emhj.20.018
- Gbagbo FY, Ameyaw EK, Yaya S. Artificial intelligence and sexual reproductive health and rights: A technological leap towards achieving Sustainable Development Goal 3.7. Reprod Health. 2024;21(1):196. Available from: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1186/s12978-024-01924-9
- Georgetown University Institute for Reproductive Health. Final report: Jordan family planning assessment. Washington, DC: Georgetown University Institute for Reproductive Health; 2016. Available from: https://www.irh.org/wp-content/uploads/2016/05/USAID_FP_assessment_2016_IRH_FINAL_REPORT.pdf
- Gharaibeh MK, Al-Obeisat SM, Hattab AS. Quality of life and health status of Jordanian women users of various contraceptive methods and associated factors: Implications for contraceptive policies. Patient Prefer Adherence. 2022;16:403-12. Available from: https://doi.org/10.2147/ppa.s344822
- Ghosh P, Thornton R. The mother-in-law effect: Heterogeneous impacts of counseling on family planning take-up in Jordan. Rev Econ Household. 2024. Available from: https://biglab.nd.edu/papers/the-mother-in-law-effect-heterogeneous-impacts-of-counseling-on-family-planning-take-up-in-jordan/
- Hardee K, Croce-Galis M, Gay J, Boydell V, Muhwezi DK, Gray K, et al. Improving voluntary, rights-based family planning: Experience from Nigeria and Uganda. Open Access J Contracept. 2019;10:55-67. Available from: https://doi.org/10.2147/oajc.s215945
- High Impact Practices in Family Planning (HIPs). Family planning high-impact practices list. Washington, DC: The High Impact Practices Partnership; 2022. Available from: https://www.fphighimpactpractices.org/wp-content/uploads/2020/11/HIP-list_2022.pdf
- Higher Population Council. Youth-friendly reproductive health services. Amman: Higher Population Council; 2017. Available from: https://www.hpc.org.jo/sites/default/files/Youth%20Friendly%20Reproductive%20Health%20Services.pdf
- Higher Population Council. Jordan's national strategy for reproductive and sexual health 2020–2030. Amman: Higher Population Council; 2020. Available from: https://www.hpc.org.jo/sites/default/files/JORDAN%27S%20NATIONAL%20STRATEGY.pdf
- Human Rights Watch. Jordan: End child marriage in status talks [Internet]. New York: Human Rights Watch; 2019 Apr 3 [cited 2024 Dec 5]. Available from: https://www.hrw.org/news/2019/04/03/jordan-end-child-marriage-status-talks
- Jum'Ah D, Binsaleh AY, Shilbayeh SA, Halboup A, Abu-Farha R. Perceptions and practices of community pharmacists regarding emergency contraceptives in Jordan: A qualitative study. Afr J Reprod Health. 2025;29(3):115-24. Available from: https://doi.org/10.29063/ajrh2025/v29i3.14
- Kamhawi S, Underwood C, Murad H, Jabre B. Client-centered counseling improves client satisfaction with family planning visits: Evidence from Irbid, Jordan. Glob Health Sci Pract. 2013;1(2):180-92. Available from: https://doi.org/10.9745/ghsp-d-12-00051
- Kapoor NR, Bhatia V, Hamed L, Tiltnes A, Abu Hamad B. Healthcare practitioners' experiences in delivering sexual and reproductive health services to unmarried adolescent clients in Jordan. BMC Health Serv Res. 2022;22(1):31. Available from: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1186/s12913-021-07415-y
- Komasawa M, Aoyama A, Shirayama Y, Sato M, Komasawa Y, Alouri M. Demand for family planning satisfied with modern methods and its associated factors among married women of reproductive age in rural Jordan. PLoS One. 2020;15(3):e0230421. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0230421
- Mahadeen AI, Khalil AO, Hamdan-Mansour AM, Sato T, Imoto A. Knowledge, attitudes and practices towards family planning among women in the rural southern region of Jordan. East Mediterr Health J. 2012;18(6):567-72. Available from: https://doi.org/10.26719/2012.18.6.567
- Mahasneh I, Ebrahim F. The epidemiological decline in the human fertility rate in the Arab world over the 10-year period 2011–2021. Middle East Fertil Soc J. 2024;29(1):47. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1186/s43043-024-00205-6
- MannionDaniels. Raising awareness and overcoming challenges to achieving comprehensive sexual and reproductive health in Jordan. The Hague: NWO; 2020 Aug. Available from: https://www.nwo.nl/sites/nwo/files/documents/SRHR%20-%20Joint%20policy%20brief%20-%20Jordan.pdf
- MannionDaniels, Nemr C, Share-Net Jordan/Higher Population Council. Report for Jordan SRHR workshop. The Hague: NWO; 2020. Available from: https://www.nwo.nl/sites/nwo/files/documents/SRHR%20Report%20Jordan%20Workshop%202020.pdf
- Mickler AK, Welz T, Lahn J, Froeschl G, May AV, Greaney J. Applications of the high-impact practices in family planning during COVID-19. Sex Reprod Health Matters. 2021;29(1):9-17. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1080/26410397.2021.1881210
- Moazzam A. Ensuring contraceptive security through effective supply chains. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2017. Available from: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/WHO-RHR-17.09
- Moazzam A, Bellows B. Ensuring adequate financing of family planning commodities and services: Family planning evidence brief. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2018. Available from: https://knowledgecommons.popcouncil.org/departments_sbsr-rh/219/
- Morris CN, Gribble JN, Vander Velde N. When political solutions for acute conflict in Yemen seem distant, demand for reproductive health services is immediate: A programme model for resilient family planning and post-abortion care services. Sex Reprod Health Matters. 2019;27(2):100-11. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1080/26410397.2019.1610279
- Mourtada R, Melnikas AJ. Crisis upon crisis: A qualitative study exploring the joint effect of the political, economic, and pandemic challenges in Lebanon on Syrian refugee women's fertility preferences and behaviour. Confl Health. 2022;16(1):35. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13031-022-00468-8
- Chowdhury NF, Haque MJ, Jahan MS, Rashid MAM, Mostafa MG, Rashid F. Knowledge, beliefs, and preventive practices regarding dengue among rural communities in Bangladesh. KYAMC J. 2024;15(3). Available from: https://www.banglajol.info/index.php/KYAMCJ/article/view/75223
- Chowdhury SMMH, Rashid MA, Trisha SY, Ibrahim M, Hossen MS. Dengue investigation research in Bangladesh: Insights from a scoping review. Health Sci Rep. 2025;8(3):e70568. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1002/hsr2.70568
- Pure E, Husna ALA, Rokony S, Thowai AS, Moulee ST, Jahan A, et al. Knowledge, attitude, and practices regarding dengue infection: A community-based study in rural Cox’s Bazar. J Commun Dis. 2025;57(1):121-30. Available from: https://medical.advancedresearchpublications.com/index.php/Journal-CommunicableDiseases/article/view/4186
- Mohiuddin AK. Dengue protection and cure: Bangladesh perspective. Eur J Sustain Dev Res. 2019;4(1):em0104. Available from: https://www.ejosdr.com/download/dengue-protection-and-cure-bangladesh-perspective-6260.pdf
- Al-Amin HM, Johora FT, Irish SR, Hossainey MR, Vizcaino L, Paul KK, et al. Insecticide resistance status of Aedes aegypti in Bangladesh. Parasit Vectors. 2020;13(1):622. Available from: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1186/s13071-020-04503-6
- Al-Amin HM, Gyawali N, Graham M, Alam MS, Lenhart A, Hugo LE, et al. Insecticide resistance compromises the control of Aedes aegypti in Bangladesh. Pest Manag Sci. 2023;79(8):2846-61. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1002/ps.7462
- Hossain S, Islam MdM, Hasan MdA, Chowdhury PB, Easty IA, Tusar MdK, et al. Association of climate factors with dengue incidence in Bangladesh, Dhaka City: A count regression approach. Heliyon. 2023;9(5):e16053. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e16053
- Paul R, Fincher C. Bangladesh sees worst single-day surge in dengue cases and deaths this year. Reuters. 2025. Available from: https://www.reuters.com/business/healthcare-pharmaceuticals/bangladesh-sees-worst-single-day-surge-dengue-cases-deaths-this-year-2025-09-21/
- Rahman A. Dengue deaths up 150%, cases double compared to last year. Bonik Barta. 2025 Sep 22. Available from: https://en.bonikbarta.com/bangladesh/YrVF5I54veNNyeTR
- UNB. 8 more dead, 778 hospitalised as Bangladesh fails to curb dengue. United News of Bangladesh. 2025. Available from: https://www.dhakatribune.com/bangladesh/health/397128/8-more-dead-778-hospitalized-as-bangladesh-fails
- Paul R. Dengue cases surge across Bangladesh as experts call for urgent action. Reuters. 2025. Available from: https://www.reuters.com/business/healthcare-pharmaceuticals/dengue-cases-surge-across-bangladesh-experts-call-urgent-action-2025-10-07/
- DGHS/UNICEF. Dengue Dynamic Dashboard for Bangladesh. Health Emergency Operation Center & Control Room, Directorate General of Health Services. Accessed 2025 Dec 8.
- News Desk. Dengue: Four more die, 920 hospitalised in 24 hours. Daily Sun. 2025. Available from: https://www.daily-sun.com/national/840813/dengue-four-more-die-920-hospitalised-in-24hrs
- Asaduzzaman M, Khan EA, Hasan MN, Rahman M, Ashrafi SAA, Haque F, et al. The 2023 dengue fatality in Bangladesh: Spatial and demographic insights. IJID Regions. 2025;15:100654. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijregi.2025.100654
- Hossain MS, Noman AA, Mamun SMAA, Mosabbir AA. Twenty-two years of dengue outbreaks in Bangladesh: Epidemiology, clinical spectrum, serotypes, and future disease risks. Trop Med Health. 2023;51(1):37. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1186/s41182-023-00528-6
- Barr JS, Martin LE, Tate AT, Hillyer JF. Warmer environmental temperature accelerates aging in mosquitoes, decreasing longevity and worsening infection outcomes. Immun Ageing. 2024;21:61. Available from: https://link.springer.com/article/s12979-024-00465-w
- Perdomo HD, Khorramnejad A, Cham NM, Kropf A, Sogliani D, Bonizzoni M. Prolonged exposure to heat enhances mosquito tolerance to viral infection. Commun Biol. 2025;8:168. Available from: https://www.nature.com/articles/s42003-025-07617-8
- Jacobo J. Mosquitoes found in Iceland for 1st time as temperatures in the region rise. ABC News. 2025. Available from: https://abcnews.go.com/International/mosquitoes-found-iceland-1st-time-temperatures-region-rise/story?id=126716295
- Galeana-Pizaña JM, Cruz-Bello GM, Caudillo-Cos CA, Jiménez-Ortega AD. Impact of deforestation and climate on the spatio-temporal spread of dengue fever in Mexico. Spat Spatio-Temporal Epidemiol. 2024;50:100679. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sste.2024.100679
- Andrade AC, Falcão LA, Borges MA, Leite ME, Espírito Santo MM. Are land use and cover changes and socioeconomic factors associated with the occurrence of dengue fever? A case study in Minas Gerais State, Brazil. Resources. 2024;13(3):38. Available from: https://doi.org/10.3390/resources13030038
- Chaves LS, Conn JE, López RV, Sallum MA. An abundance of impacted forest patches <5 km² is a key driver of the incidence of malaria in Amazonian Brazil. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):7077. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-25344-5
- Nawar N, Sorker R, Chowdhury FJ, Mostafizur Rahman Md. Present status and historical changes of urban green space in Dhaka City, Bangladesh: A remote sensing driven approach. Environ Chall. 2022;6:100425. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envc.2021.100425
- IIED. Hot Cities: Dhaka. London: International Institute for Environment and Development; 2024 June.
- World Bank. Bangladesh faces health and economic risks from rising temperatures. Press Release. 2025 Sep 16. Available from: https://www.worldbank.org/en/news/press-release/2025/09/16/bangladesh-faces-health-and-economic-risks-from-rising-temperature-world-bank
- Banu S, Hu W, Guo Y, Hurst C, Tong S. Projecting the impact of climate change on dengue transmission in Dhaka, Bangladesh. Environ Int. 2014;63:137-42. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2013.11.002
- Quam J, Campbell S. South Asia: Urban Geography I – Dhaka. In: The Eastern World: Daily Readings on Geography. College of DuPage Digital Press; 2022. Available from: https://cod.pressbooks.pub/easternworlddailyreadingsgeography/
- UNB. Dhaka world’s 2nd largest city with 36.6 million: UN. The Daily Star. 2025 Nov 26. Available from: https://www.thedailystar.net/news/bangladesh/news/dhaka-worlds-2nd-largest-city-366m-people-un-report-4043976
- Sultana A, Islam A, Hosna A, Tahsin A, Islam A. The impact of urbanization on the proliferation of Aedes aegypti (Diptera: Culicidae) mosquito population in Dhaka Mega City, Bangladesh. Bangladesh J Zool. 2024;52(2):201-15. Available from: https://doi.org/10.3329/bjz.v52i2.77460
- Kamal AS, Al-Montakim MdN, Hasan MdA, Mitu MMP, Gazi MY, Uddin MM, et al. Relationship between urban environmental components and dengue prevalence in Dhaka City—An approach of spatial analysis of satellite remote sensing, hydro-climatic, and census dengue data. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023;20(5):3858. Available from: https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20053858
- Roy S, Biswas A, Shawon MT, Akter S, Rahman MM. Land use and meteorological influences on dengue transmission dynamics in Dhaka City, Bangladesh. Bull Natl Res Cent. 2024;48:32. Available from: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1186/s42269-024-01188-0
- Inspira Advisory and Consulting Limited. Challenges of slum living in Bangladesh: A closer look at WASH inequities in Bangladesh’s slums. Inspira-bd.com. 2023 Jul 17.
- Paulson W, Kodali NK, Balasubramani K, Dixit R, Chellappan S, Behera SK, et al. Social and housing indicators of dengue and chikungunya in Indian adults aged 45 and above: Analysis of a nationally representative survey (2017–18). Arch Public Health. 2022;80(1):125. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13690-022-00868-5
- UNICEF. 230 tons of fecal waste end up in open water bodies in Dhaka daily — UNICEF and WaterAid call for stronger sanitation management. UNICEF Bangladesh. 2025 Feb 25. Available from: https://www.unicef.org/bangladesh/en/press-releases/230-tons-fecal-waste-end-open-water-bodies-bangladesh-daily-unicef-and-wateraid-call
- Alam HMN. Dhaka’s drains, dengue, and denial. The Daily Star. 2025 Jul 10. Available from: https://www.thedailystar.net/opinion/views/news/dhakas-drains-dengue-and-denial-3935806
- Islam J, Asif MH, Rahman S, Hasan M. Exploring mosquito hazards in Bangladesh: Challenges and sustainable solutions. IUBAT Rev. 2024;7(2):1–29. Available from: https://banglajol.info/index.php/IUBATR/article/view/78792
- Nature India. Poor access to tap water linked to dengue risk. 2021. Available from: https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2021/02/210211144428.htm
- UNB. A roundtable discussion on ‘Solid Waste Management – Challenges and Solutions for Bangladesh’. United Nations Bangladesh. 2024 Oct 3. Available from: https://please-project.org/resource/high-level-roundtable-discussion-on-plastic-waste-management-challenges-and-solutions-in-bangladesh/
- Sasi MS, Lal N. The impact of solid waste management practices on vector-borne disease risk in Thiruvananthapuram. Int J Multidiscip Res. 2024;6(4):1-10. Available from: https://www.ijfmr.com/research-paper.php?id=26724
- Rosser JI, Openshaw JJ, Lin A, Taruc RR, Tela A, Tamodding N, et al. Seroprevalence, incidence estimates, and environmental risk factors for dengue, chikungunya, and Zika infection amongst children living in informal urban settlements in Indonesia and Fiji. BMC Infect Dis. 2025;25(1):51. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12879-024-10315-1
- World Health Organization. Climate change, pollution, and health: Impact of chemicals, waste, and pollution on human health. Executive Board EB154/24. Geneva: WHO; 2023 Dec 18. Available from: https://apps.who.int/gb/ebwha/pdf_files/EB154/B154_24-en.pdf
- Lu HC, Lin FY, Huang YH, Kao YT, Loh EW. Role of air pollutants in dengue fever incidence: Evidence from two southern cities in Taiwan. Pathog Glob Health. 2022;117(6):596-604. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1080/20477724.2022.2135711
- Mailepessov D, Ong J, Aik J. Influence of air pollution and climate variability on dengue in Singapore: A time-series analysis. Sci Rep. 2025;15(1):13467. Available from: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-025-97068-2
- Ju X, Zhang W, Yimaer W, Lu J, Xiao J, Qu Y, et al. How air pollution altered the association of meteorological exposures and the incidence of dengue fever. Environ Res Lett. 2022;17(12):124041. Available from: https://iopscience.iop.org/article/10.1088/1748-9326/aca59f/meta
- Thongtip S, Sapbamrer P, Chaichanan P, Chiablam S, Pimonsree S. Association of meteorology and air quality with dengue fever incidence in upper northern Thailand. EnvironmentAsia. 2025;18(1):164-73. Available from: https://doi.org/10.14456/ea.2025.13
- Mohammad AKH, Che Dom N, Do Camalxaman S, Syed Ismail SN. Correlational analysis of air pollution index levels on dengue surveillance data: A retrospective study in Melaka, Malaysia. J Sustain Sci Manag. 2020;15(8):1-9. Available from: https://jssm.umt.edu.my/wp-content/uploads/2020/12/10-15.8.pdf
- Carneiro MAF, Alves BCA, Gehrke FS, Domingues JN, Sá N, Paixão S, et al. Influence of environmental factors on dengue-reported cases. Rev Assoc Med Bras. 2017;63(11):957-61. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1590/1806-9282.63.11.957
- Tewari P, Ma P, Gan G, Janhavi A, Choo ELW, Koo JR, et al. Non-linear associations between meteorological factors, ambient air pollutants, and major mosquito-borne diseases in Thailand. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2023;17(12):e0011763. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pntd.0011763
- Maquart P-O, Froehlich Y, Boyer S. Plastic pollution and infectious diseases. Lancet Planet Health. 2022;6(10):e842-e845. Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36208647/
- Afroze CA, Ahmed MN, Azam MN, Jahan R, Rahman H. Microplastics pollution in Bangladesh: A decade of challenges, impacts, and pathways to sustainability. Integr Environ Assess Manag. 2025 Aug 11. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1093/inteam/vjaf108
- Meijer LJJ, van Emmerik T, van der Ent R, Schmidt C, Lebreton L. More than 1000 rivers account for 80% of global riverine plastic emissions into the ocean. Sci Adv. 2021;7(18):eaaz5803. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.aaz5803
- Environment and Social Development Organization (ESDO). Huge use of poly bags: 78 thousand tons of waste in a year. ESDO [Internet]. 2021 Jun 5. Available from: https://esdo.org/
- Chowdhury SI. Urban per capita plastic use is 9 kg, 24 kg in Dhaka. New Age [Internet]. 2021 Dec 20. Available from: https://www.newagebd.net/article/157775/urban-per-capita-plastic-use-9kg-24kg-in-dhaka
- Li JH, Liu XH, Liang GR, Gao HT, Guo SH, Zhou XY, et al. Microplastics affect mosquitoes from aquatic to terrestrial lifestyles and are transferred to mammals through mosquito bites. Sci Total Environ. 2024;917:170547. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2024.170547
- Shopon HU-R. Dhaka: Unplanned city faces a grand spectacle of risks [Internet]. Deutsche Welle. 2025 Jul 23. Bengali.
- Hassan A. Building faults are overlooked if officials are appeased. Prothom Alo [Internet]. 2024 Mar 9. Available from: https://en.prothomalo.com/bangladesh/km0ki6cevl
- Tribune Desk. Potential Aedes breeding grounds were found in 70% DNCC homes. Dhaka Tribune [Internet]. 2020 Jul 4. Available from: https://www.dhakatribune.com/bangladesh/dhaka/215149/potential-aedes-breeding-grounds-found-in-70%25-dncc
- Staff Correspondent. Greetings and promises on our 15th anniversary: Aedes reproduction—high rises are mainly responsible. Daily Sun [Internet]. 2021 May 6. Available from: https://www.daily-sun.com/printversion/details/835258
- TBS Report. Construction work will be halted if Aedes larvae are found on the site, Mayor Taposh. The Business Standard [Internet]. 2024 Apr 25. Available from: https://www.tbsnews.net/bangladesh/construction-work-will-be-halted-if-aedes-larvae-found-site-mayor-taposh-835591
- Staff Correspondent. Dengue infection: 13 Dhaka wards at high risk. The Daily Star [Internet]. 2025 Jun 19. Available from: https://www.thedailystar.net/news/bangladesh/news/dengue-infection-13-dhaka-wards-high-risk-3920606
- Kamal M, Sultana R, Julkarnayeen M. Dengue crisis prevention and control: governance challenges and way forward. Transparency International Bangladesh [Internet]. 2023 Oct 30. Available from: https://www.ti-bangladesh.org/images/2023/report/dengue-crisis/Executive-Study-EN-Dengue-Crisis-Prevention-and-Control-TIB.pdf
- Islam MdJ. Dengue rages as TK1,000CR lost to futile mosquito control efforts. The Business Standard [Internet]. 2025 Nov 16. Available from: https://www.tbsnews.net/bangladesh/dengue-rages-tk1000cr-lost-futile-mosquito-control-efforts-1286616
- Hossain M, Rakib MS, Hasan MM, Powshi SN, Islam E, Islam NN. The 2023 dengue outbreak in Bangladesh: an epidemiological update. Health Sci Rep. 2025;8(5):e70852. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1002/hsr2.70852
- TBS Report. Dhaka South increases mosquito control budget amid rising dengue infections, reports revenue growth. The Business Standard [Internet]. 2025 Aug 6. Available from: https://www.tbsnews.net/bangladesh/dhaka-south-increases-mosquito-control-budget-amid-rising-dengue-infections-reports
- Vourc’h G, Plantard O, Morand S. How does biodiversity influence the ecology of infectious disease? In: New Frontiers of Molecular Epidemiology of Infectious Diseases. 2011. p. 291–309. Available from: https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-94-007-2114-2_13
- Sommese F. Nature-based solutions to enhance urban resilience in the climate change and post-pandemic era: a taxonomy for the built environment. Buildings. 2024;14(7):2190. Available from: https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings14072190
- World Health Organization. Vector management and delivery of vector control services. In: Dengue: Guidelines for Diagnosis, Treatment, Prevention and Control: New Edition. Geneva (Switzerland): World Health Organization; 2009. p. 57–86. Available from: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789241547871
- Sim S, Ng LC, Lindsay SW, Wilson AL. A greener vision for vector control: the example of the Singapore dengue control programme. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2020;14(8):e0008428.
- De Oliveira Lemos L, Oscar Júnior AC, de Assis Mendonça F. Urban climate maps as a public health tool for urban planning: the case of dengue fever in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. Urban Climate. 2021;35:100749. Available from: https://ui.adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/2021UrbCl..3500749D/abstract
- Arunachalam N, Tyagi BK, Samuel M, Krishnamoorthi R, Manavalan R, Tewari SC, et al. Community-based control of Aedes aegypti by adoption of eco-health methods in Chennai City, India. Pathog Glob Health. 2012;106(8):488–496. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1179/2047773212y.0000000056
- The Times of India. Bengaluru deploys 700 volunteers, 240 inspectors to curb rising dengue cases. The Times of India [Internet]. 2025 May 22. Available from: https://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/city/bengaluru/bengaluru-deploys-700-volunteers-240-inspectors-to-curb-rising-dengue-cases/articleshow/121323723.cms
- Ane RL, Herbuela VRDM, Wahid I, Susilawaty A. Influence of water supply conditions and water storage containers on Aedes mosquito abundance in Makassar City, Indonesia. Research Square [Preprint]. 2021. Available from: https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-189214/v1
- Agus Nurjana M, Srikandi Y, Wijatmiko TJ, Hidayah N, Isnawati R, Octaviani O, et al. Water containers and the preferred conditions for laying eggs by Aedes mosquitoes in Maros Regency, South Sulawesi, Indonesia. J Water Health. 2023;21(11):1741–1746. Available from: https://doi.org/10.2166/wh.2023.270
- Tana S, Umniyati S, Petzold M, Kroeger A, Sommerfeld J. Building and analyzing an innovative community-centered dengue-ecosystem management intervention in Yogyakarta, Indonesia. Pathog Glob Health. 2012;106(8):469–478. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1179/2047773212y.0000000062
- Gibb R, Colón-González FJ, Lan PT, Huong PT, Nam VS, Duoc VT, et al. Interactions between climate change, urban infrastructure, and mobility are driving dengue emergence in Vietnam. Nat Commun. 2023;14(1):8179. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-023-43954-0
- Jency PJ, Rishla KE, Jabir MM, Vijayakumar B, Dinesh RJ, Dhanalakshmi R. Anti-dengue sanitation practices: a health education approach for municipal sanitary workers in Puducherry, India. Cureus. 2024;16(7):e65227. Available from: https://doi.org/10.7759/cureus.65227
- Abeyewickreme W, Wickremasinghe AR, Karunatilake K, Sommerfeld J, Axel K. Community mobilization and household-level waste management for dengue vector control in Gampaha district of Sri Lanka: an intervention study. Pathog Glob Health. 2012;106(8):479–487. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1179/2047773212y.0000000060
- Dhaka North City Corporation. Dhaka North City Corporation active tender list. Database of Government Tenders of Dhaka North City Corporation [Internet]. Accessed 2026 Jan 6. Available from: https://dorpatra.com
- Hossain S, Mostafa M. Huge funds to prevent waterlogging go down the drain. Prothom Alo [Internet]. 2020 Jul 27. Available from: https://en.prothomalo.com/bangladesh/government/huge-funds-to-prevent-water-logging-go-down-the-drain
- UNB. Despite multiple master plans and spending over Tk 750 crore, Dhaka’s waterlogging crisis persists. The Business Standard [Internet]. 2024 Sep 20. Available from: https://www.tbsnews.net/bangladesh/despite-multiple-master-plans-and-spending-over-tk-750-crore-dhakas-waterlogging-crisis
- Nandy D. Tk 10cr for a food court, Tk 1cr for toilet! The Daily Star [Internet]. 2025 Apr 5.
- Roney M. Dhaka’s drainage problem. The Financial Express [Internet]. 2024 Jul 30. Available from: https://today.thefinancialexpress.com.bd/editorial/dhakas-drainage-problem-1722263785
- Al Amin M. WASA's investment to solve waterlogging goes down the drain. The Business Standard [Internet]. 2021 Jan 26. Available from: https://www.tbsnews.net/bangladesh/wasa-investment-solve-waterlogging-goes-down-drain-191779
- World Health Organization. Dengue: Guidelines for Diagnosis, Treatment, Prevention and Control. New ed. Geneva (Switzerland): World Health Organization; 2009. Chapter 3, Vector management and delivery of vector control services. Available from: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789241547871
- Mowla QA, Islam MS. Natural drainage system and water logging in Dhaka: measures to address the problems. J Bangladesh Inst Planners. 2013;6:23–33. Available from: https://www.bip.org.bd/admin/uploads/bip-publication/publication-11/paper/20141016154547.pdf
- Alam S, Rahman A, Yunus A. Designing stormwater drainage network for urban flood mitigation using SWMM: a case study on Dhaka City of Bangladesh. Am J Water Resour. 2023;11(2):65–78. Available from: https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Siam-Alam/publication/371947202_Designing_Stormwater_Drainage_Network_for_Urban_Flood_Mitigation_using_SWMM_A_Case_Study_on_Dhaka_City_of_Bangladesh/links/649d5a27c41fb852dd3e56fa/Designing-Stormwater-Drainage-Network-for-Urban-Flood-Mitigation-using-SWMM-A-Case-Study-on-Dhaka-City-of-Bangladesh.pdf
- Castro MC, Kanamori S, Kannady K, Mkude S, Killeen GF, Fillinger U. The importance of drains for the larval development of lymphatic filariasis and malaria vectors in Dar es Salaam, United Republic of Tanzania. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2010;4(5):e693. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pntd.0000693
- Charlesworth SM, Kligerman DC, Blackett M, Warwick F. The potential to address disease vectors in favelas in Brazil using sustainable drainage systems: Zika, drainage, and greywater management. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022;19(5):2860. Available from: https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19052860
- Rania P, Junaid Y. Analysis of the relationship between waste management systems and dengue fever cases in urban areas. Magenta J Healthymedi. 2025;2(4):179–192. Available from: https://doi.org/10.37899/mjdh.v2i4.291
- Bertacco EAM, Prestes-Carneiro LE, de Araújo RR, D'Andrea LAZ, Pinheiro LS, Flores EF. Impact of storm drains on the maintenance of dengue endemicity in Presidente Prudente, São Paulo, Brazil: a geospatial and epidemiologic approach. Front Public Health. 2024;12:1442622. Available from: https://doi.org/10.3389/fpubh.2024.1442622
- Souza RL, Mugabe VA, Paploski IAD, Rodrigues MS, Moreira PSDS, Nascimento LCJ, et al. Effect of an intervention in storm drains to prevent Aedes aegypti reproduction in Salvador, Brazil. Parasites Vectors. 2017;10:328. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13071-017-2266-6
- Bhardwaj N. After water, MC to privatise sewerage maintenance. The Times of India. 2025 Sep 13. Available from: https://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/city/ludhiana/after-water-mc-to-privatise-sewerage-maintenance/articleshow/123857990.cms
- Kayesh MEH, Khalil I, Kohara M, Tsukiyama-Kohara K. Increasing dengue burden and severe dengue risk in Bangladesh: An overview. Trop Med Infect Dis. 2023;8(1):32. Available from: https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed8010032
- Dhaka Tribune. WHO expert: Fogging won’t help destroy Aedes. 2025 Apr 8. Available from: https://www.dhakatribune.com/bangladesh/dhaka/184177/who-expert-fogging-won%E2%80%99t-help-destroy-aedes
- Low GK, Jiee SF, Lim SH, Omosumwen OF, Shanmuganathan S. The effectiveness of dengue vector control: A meta-review. Trop Med Int Health. 2025;30(10):1069-86. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1111/tmi.70018
- Al Noman A, Das D, Nesa Z, Tariquzzaman M, Sharzana F, Rakibul Hasan M, et al. Importance of Wolbachia-mediated biocontrol to reduce dengue in Bangladesh and other dengue-endemic developing countries. Biosaf Health. 2023;5(2):69-77. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bsheal.2023.03.003
- Martini M, Adi MS. Ovitrap training improves dengue hemorrhagic fever control. Jurnal Empathy Pengabdian Kepada Masyarakat. 2025;6(1):23-29. Available from: https://doi.org/10.37341/jurnalempathy.v6i1.288
- Guo X, Liu S, Liu X, Chen K, Chen W, Huang Z, et al. An improved ovitrap-based surveillance framework: Facilitating cost-efficient monitoring and efficacy assessment of integrated vector management strategies for dengue outbreak control. Parasites Vectors. 2025;18:380. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13071-025-07002-8
- Smith Gueye C, Newby G, Gosling RD, Whittaker MA, Chandramohan D, Slutsker L, et al. Strategies and approaches to vector control in nine malaria-eliminating countries: A cross-case study analysis. Malar J. 2016;15:2. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12936-015-1054-z
- Beier JC, Keating J, Githure JI, Macdonald MB, Impoinvil DE, Novak RJ. Integrated vector management for malaria control. Malar J. 2008;7(Suppl 1):S4. Available from: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1186/1475-2875-7-S1-S4
- Saadatian-Elahi M, Rabilloud M, Möhlmann TWR, Langlois-Jacques C, Ariffin FD, et al. Effectiveness of integrated vector management on the incidence of dengue in urban Malaysia: A cluster-randomised controlled trial. Lancet Infect Dis. 2025;25(9):977-85. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1016/S1473-3099(25)00086-6
- Hapugoda M, Gunawardene NS, Ranathunge T, Samaraweera S, Karunathilake K, Sow BBD, et al. Suppression of Aedes albopictus in Sri Lanka using the sterile insect technique with a sustained effect. Parasite. 2025;32:59. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1051/parasite/2025050
- Sapkota S. Effectiveness of integrated vector management for controlling Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus mosquitoes and managing dengue in Tharu Village, Chitwan, Nepal. Intergovernmental Research and Policy Journal (IRPJ). 2025 Jul 21.
- Chanda E, Masaninga F, Coleman M, Sikaala C, Katebe C, MacDonald M, et al. Integrated vector management: the Zambian experience. Malar J. 2008;7:164. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1186/1475-2875-7-164
- Alam KF, Islam T. A critical analysis of the Bangladesh national dengue prevention and control strategy (2024–2030): a comprehensive roadmap in an era of climate change. SSB Global J Med Sci. 2025;6(02):26–29. Available from: https://doi.org/10.61561/ssbgjms.v6i02.99
- Osail SM, Sanny SI, Zerin T. A narrative review of dengue disaster in Bangladesh: unprecedented outbreak and management failure. J Bacteriol Virol. 2024;54(2):63–75. Available from: https://journal-jbv.apub.kr/articles/article/M2eZ/
- FE Report. Fragile health care fails to address dengue crisis: TIB. The Financial Express [Internet]. 2023 Oct 31. Available from: https://thefinancialexpress.com.bd/health/only-61pc-dengue-diagnosis-cases-represented-as-complete-dengue-picture-tib-study
- Alam H, Adhikary TS. Dengue outbreak: patients from outside swarm city hospitals. The Daily Star [Internet]. 2025 Jun 24. Available from: https://www.thedailystar.net/news/bangladesh/news/dengue-outbreak-patients-outside-swarm-city-hospitals-3924116
- Editorial. Barguna’s dengue crisis is exposing public health gaps. The Daily Star [Internet]. 2025 Jun 26. Available from: https://www.thedailystar.net/opinion/editorial/news/bargunas-dengue-crisis-exposing-public-health-gaps-3926841
- Billah M, Shampa N, Henderson A. Escalating dengue burden and emerging hotspots in Bangladesh: a decade of trends and 2025 forecast. Int J Data Sci Anal. 2025;11(5):136–142. Available from: https://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/article/10.11648/j.ijdsa.20251105.12
- World Health Organization. Dengue clinical management: facilitator’s training manual. Geneva (Switzerland): World Health Organization; 2013. Available from: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789290616221
- Salehi M, Mousa Farkhani E, Moghri J, Ghasemian A, Tabatabaee SS, Hooshmand E. Global dengue fever management in health systems: identifying strategies, challenges and solutions—a scoping review protocol. BMJ Open. 2025;15(4):e097085. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2024-097085
- Ambas J, Kamesyworo K, Lidiyawati H. The role of community health nurses in handling dengue fever outbreaks in residential areas. Oshada. 2024;1(4):45–60. Available from: https://doi.org/10.62872/yaf58r34
- Suwanbamrung C, Le CN, Maneerattanasak S, Satian P, Talunkphet C, Nuprasert Y, et al. Developing and using a dengue patient care guideline for patients admitted from households to primary care units and the district hospital: a community participatory approach in southern Thailand. One Health. 2020;10:100168. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.onehlt.2020.100168
- Nontapet O, Maneerattanasak S, Jaroenpool J, Phumee A, Krachai W, Napet P, et al. Understanding dengue solution and larval indices surveillance system among village health volunteers in high- and low-risk dengue villages in southern Thailand. One Health. 2022;15:100440. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.onehlt.2022.100440
- Usmani NG, Chandra P, Hassan T, Debnath SC, Md SM, Amin B, et al. Exploring knowledge, attitudes, and practices regarding dengue fever among university students in Bangladesh: a cross-sectional study. Health Sci Rep. 2025;9(1):e71714. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1002/hsr2.71714
- Billah AHM. Dengue fever awareness: combating the menace in Bangladesh. Press Information Department, Government of the People’s Republic of Bangladesh [Internet]. 2023 Aug 9. Available from: https://pressinform.portal.gov.bd/sites/default/files/files/pressinform.portal.gov.bd/page/50aa82ee_7a92_4aa7_817b_bb323c098833/2023-08-09-05-27-b5965ce7e7a9038308e0658c71fca185.pdf
- Sarkar SR, Ray NC. Dengue fever: a public health threat to Bangladesh. Community Based Med J. 2024;13(2):282–289. Available from: https://www.banglajol.info/index.php/CBMJ/article/view/75323
- Sarker R, Roknuzzaman AS, Emon FA, Dewan SM, Hossain MdJ, Islam MdR. A perspective on the worst-ever dengue outbreak 2023 in Bangladesh: what makes this old enemy so deadly, and how can we combat it? Health Sci Rep. 2024;7(5):e2077. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1002/hsr2.2077
- Reza SB, Shoukhin MdM-U-R, Khan SA, Rahman Dewan SM. Dengue outbreak 2023 in Bangladesh: from a local concern to a global public health issue. Sci Prog. 2024;107(4):1–18. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1177/00368504241289462
- World Health Organization. Fighting dengue together: how community engagement is transforming health in Khulna City, Bangladesh. World Health Organization [Internet]. 2025 Sep 26. Available from: https://www.who.int/news-room/feature-stories/detail/fighting-dengue-together--how-community-engagement-is-transforming-health-in-khulna-city--bangladesh
- Kurniawati RD, Martini M, Wahyuningsih NE, Sutiningsih D. Integration of dengue fever prevention into school learning: an experimental study—interactive media for dengue fever prevention. Media Publikasi Promosi Kesehatan Indonesia. 2025;8(12):1590–1601. Available from: https://doi.org/10.56338/mppki.v8i12.8723
- Dsouza RP, Rodrigues DE, Saldanha PM. Effectiveness of school-based video-assisted health education program on mosquito-borne disease among upper primary children. J Health Allied Sci NU. 2022;13(01):98–102. Available from: https://www.thieme-connect.com/products/ejournals/abstract/10.1055/s-0042-1749181
- Jaroenpool J, Maneerattanasak S, Adesina F, Phumee A, Stanikzai MH, Ponprasert C, et al. A primary school-based dengue solution model for post-COVID-19 in southern Thailand: students' understanding of the dengue solution and larval indices surveillance system. PLoS One. 2024;19(12):e0313171. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0313171
- Soo WF, Gunasekaran K, Ng DX, Kwek K, Tan NC. Literacy and attitude of Asian youths on dengue and its prevention in an endemic developed community. Front Public Health. 2024;12:1361717. Available from: https://doi.org/10.3389/fpubh.2024.1361717
- Dapari R, Jumidey AQ, Manaf RA, Ahmad Zamzuri MAI, Hassan MR, Che Dom N, et al. School-based health education effect on knowledge, attitude, and practices of dengue prevention among school children: a systematic review. Discover Soc Sci Health. 2025;5(1):31. Available from: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s44155-025-00181-w
- Caprara A, Lima JW, Peixoto AC, Motta CM, Nobre JM, Sommerfeld J, et al. Entomological impact and social participation in dengue control: a cluster randomized trial in Fortaleza, Brazil. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 2015;109(2):99–105. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1093/trstmh/tru187
- Oo TS, Lin C-Y, Tsai Y-T, Laosee O, Jamaimool P, Buadit T, et al. Socio-ecological factors of dengue preventive practices among Myanmar migrants in Samut Sakhon Province, Thailand. BMC Infect Dis. 2025;25(1):1586. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12879-025-12017-8
- Ho SH, Lim JT, Ong J, Hapuarachchi HC, Sim S, Ng LC. Singapore's five decades of dengue prevention and control: implications for global dengue control. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2023;17(6):e0011400. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pntd.0011400
- Methiyothin T, Ahn I. Forecasting dengue fever in France and Thailand using XGBoost. In: Asia-Pacific Signal and Information Processing Association Annual Summit and Conference (APSIPA ASC); 2022; Chiang Mai, Thailand. p. 677–680. Available from: https://doi.org/10.23919/APSIPAASC55919.2022.9979936
- Finch E, Chang CC, Kucharski A, Sim S, Ng LC, Lowe R. Climate variation and serotype competition drive dengue outbreak dynamics in Singapore. Nat Commun. 2025;16:11364. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-025-66411-6
- Marcombe S, Chonephetsarath S, Thammavong P, Brey PT. Alternative insecticides for larval control of the dengue vector Aedes aegypti in Lao PDR: insecticide resistance and semi-field trial study. Parasit Vectors. 2018;11(1):616. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13071-018-3187-8
- de Castro Poncio L, Apolinário dos Anjos F, de Oliveira DA, de Oliveira da Rosa A, Piraccini Silva B, Rebechi D, et al. Prevention of a dengue outbreak via the large-scale deployment of sterile insect technology in a Brazilian city: a prospective study. Lancet Reg Health Am. 2023;21:100498. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lana.2023.100498
- Aira J, Olivares T, Delicado FM, Vezzani D. Mosquiot: a system based on IoT and machine learning for the monitoring of Aedes aegypti (Diptera: Culicidae). IEEE Trans Instrum Meas. 2023;72:1–13. Available from: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10093891
- Singapore National Environment Agency. Singapore facilitates collaboration on new mosquito suppression techniques on ASEAN Dengue Day. National Environment Agency (NEA) Singapore [Internet]. 2018 Jun 7. Available from: https://www.nea.gov.sg/media/news/news/index/singapore-facilitates-collaboration-on-new-mosquito-suppression-techniques-on-asean-dengue-day
- Mphande-Nyasulu FA, Yap NJ, Teo CH, Chang LY, Tay ST. Outbreak preparedness and response strategies in ASEAN member states: a scoping review. IJID Reg. 2024;12:100430. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijregi.2024.100430
- SEA-ROADS. One Health regional approach for integrated and interconnected urban dengue surveillance in Southeast Asia. UMR Espace-Dev [Internet]. 2025. Available from: https://www.pandemicpact.org/grants/P29965
- Phommasack B, Jiraphongsa C, Ko Oo M, Bond KC, Phaholyothin N, Suphanchaimat R, et al. Mekong Basin Disease Surveillance (MBDS): a trust-based network. Emerg Health Threats J. 2013;6:19944. Available from: https://doi.org/10.3402/ehtj.v6i0.19944
- Messina JP, Brady OJ, Golding N, Kraemer MUG, Wint GRW, Ray SE, et al. The current and future global distribution and population at risk of dengue. Nat Microbiol. 2019;4(9):1508–1515. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41564-019-0476-8
- Haider N, Hasan MN, Onyango J, Billah M, Khan S, Papakonstantinou D, et al. Global dengue epidemic worsens with record 14 million cases and 9000 deaths reported in 2024. Int J Infect Dis. 2025;158:107940. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijid.2025.107940
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Dengue on the rise: get the facts. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention [Internet]. 2025 May 29.
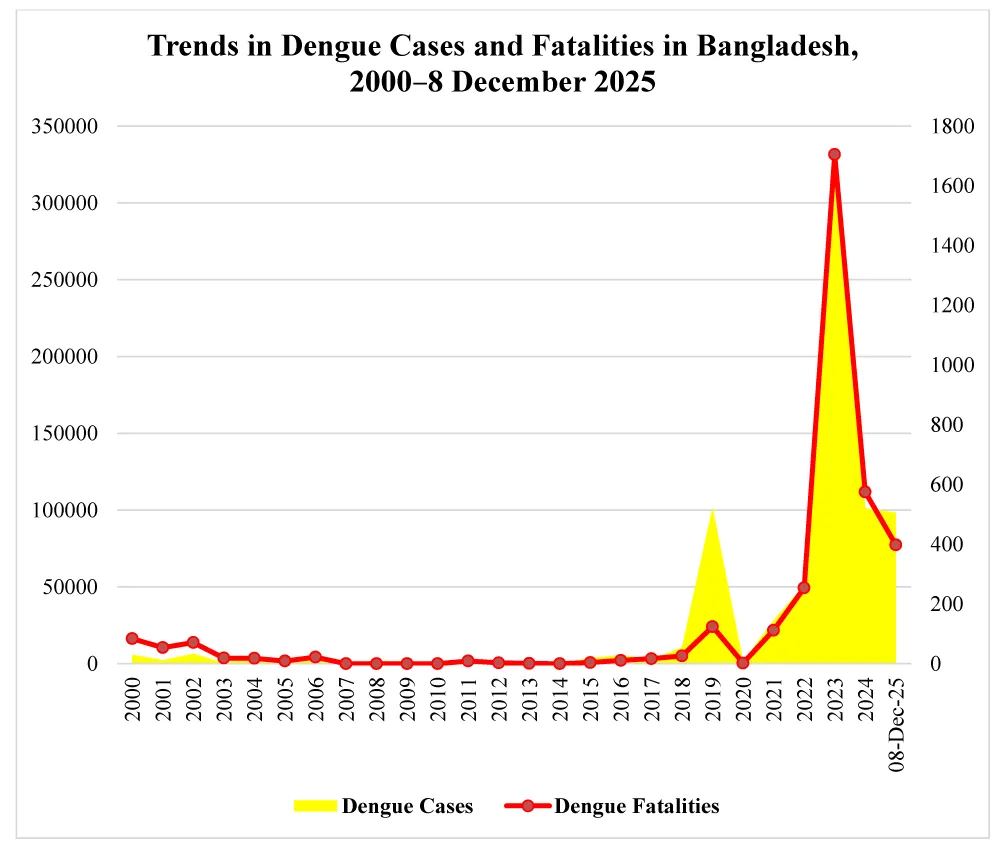
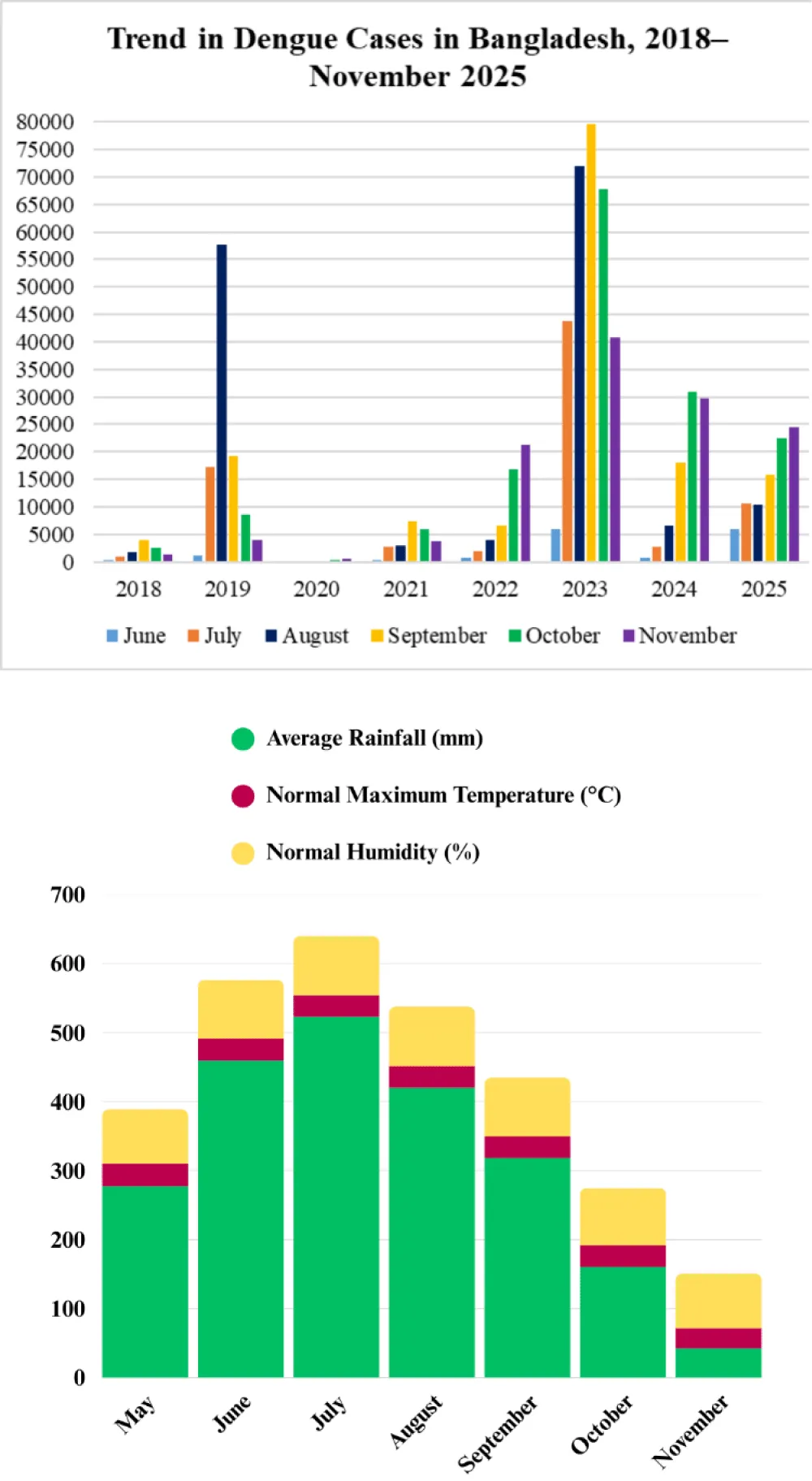
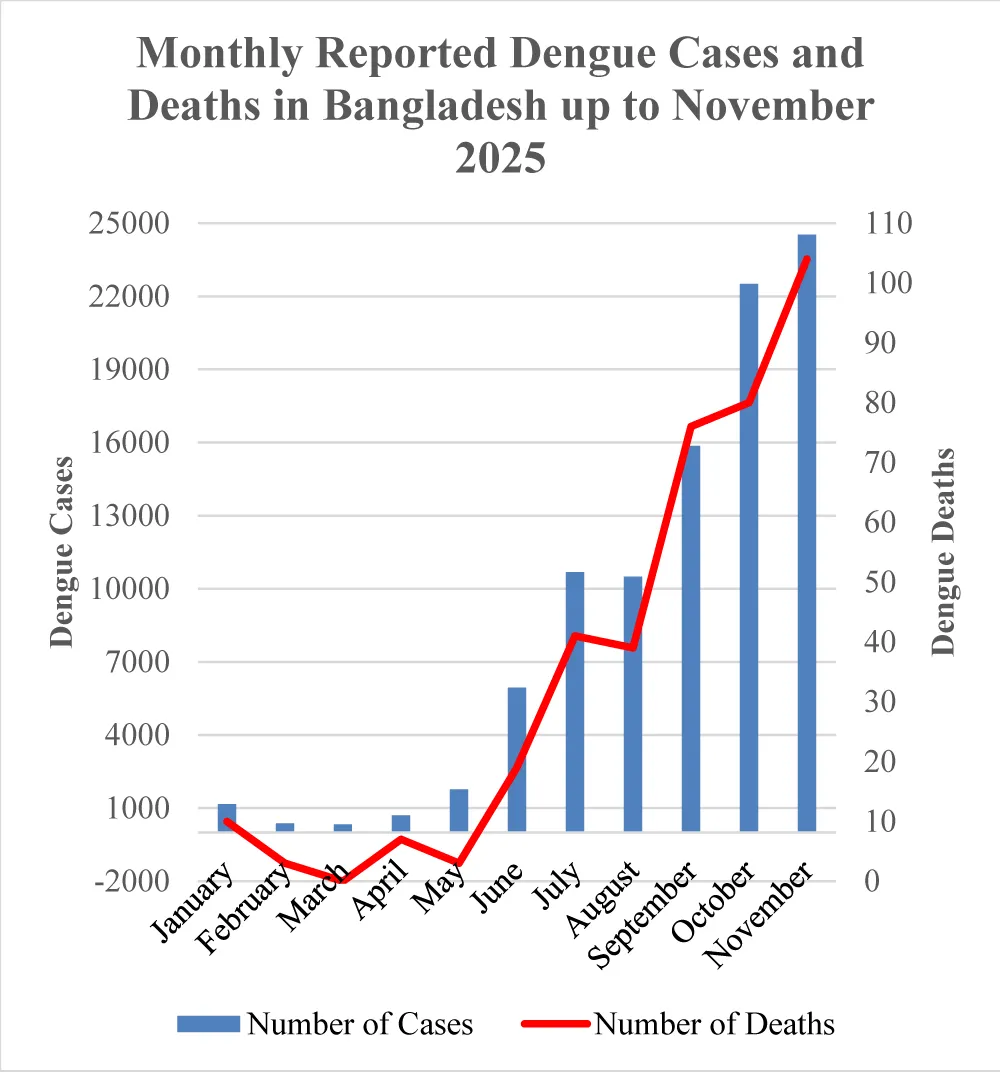
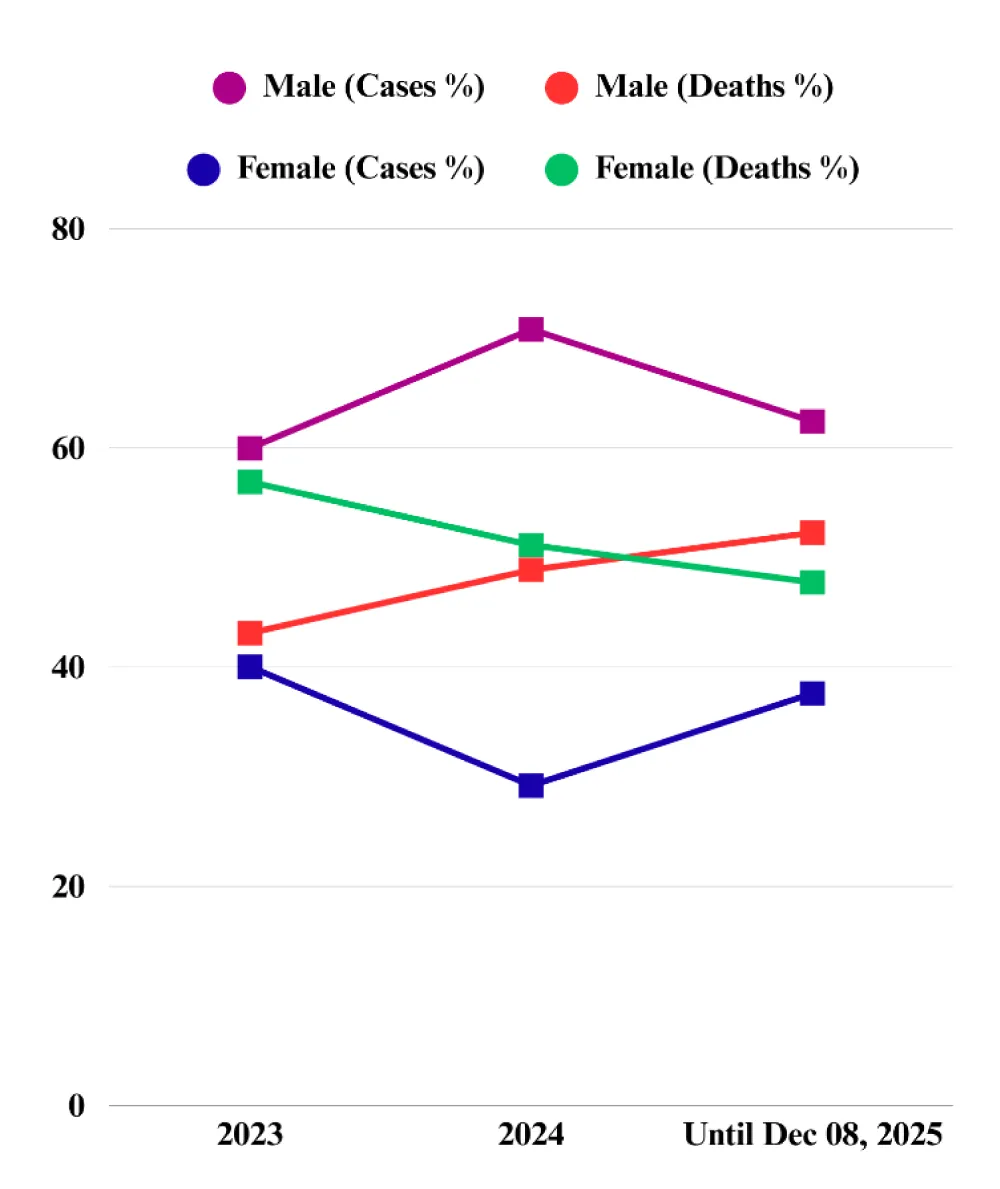



 Save to Mendeley
Save to Mendeley

